Anti-biofilm Liquid and Liquid-like Surfaces
Biofilms often form and attach to surfaces causing significant societal and economic impacts. A significant concern is biofilm infections associated with medical devices, such as catheter-associated urinary tract infections in hospitals. Anti-biofilm surfaces can use anti-microbial agents, or textured surfaces with nano-spears to rupture the bacterial cell walls and kill bacteria. However, bacteria fight back with antimicrobial resistance and by masking the surface texture.
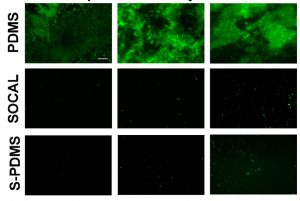
Another approach to preventing biofilm formation is to use an anti-biofilm liquid or liquid-like surface. A liquid or solid lubricant renders these surfaces slippery to bacteria so that the force from shear flow sweeps away the bacteria before a biofilm can be created. The image at the top of the page shows growth of the bacterium S. epidermidis over time on three different surfaces. There is significant growth even after 2 hours on a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) surface — which is a material commonly used in medical applications. However, the growth is significantly less on both a slippery omniphobic covalently attached liquid-like (SOCAL) surface and a PDMS surface infused with silicone oil (called S-PDMS).
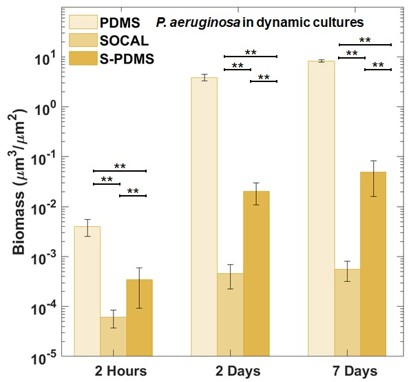
In flow situations, the SOCAL surface performs better than S-PDMS at preventing biomass growth because, unlike with the impregnated oil, it cannot be depleted from the surface [1]. The figure below shows the biomass volume of P. aeruginosa on PDMS, SOCAL and S-PDMS surfaces. This result indicates that making a surface `slippery-to-liquids’ may even be more important than the surface energy and whether the surface is hydrophobic or hydrophilic [2].
Publications
- Slippery Liquid-Like Solid Surfaces with Promising Antibiofilm Performance under Both Static and Flow Conditions Y. Zhu, G. McHale, J. Dawson, S. Armstrong, G. Wells, R. Han, H. Liu, W. Vollmer, P. Stoodley, N. Jakubovics and J. Chen, ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces 14 (2022), 6307–6319
- Long-Term Antibiofilm Efficacy of Slippery Covalently Attached Liquid-like Surfaces in Dynamic and Static Culture Conditions Y. Zhu, G. McHale, H. Barrio-Zhang, R. Han, G. G. Wells, H. Liu, R. Ledesma-Aguilar, W. Vollmer, N. Jakubovicsand J. Chen, ACS Applied Bio Materials 8 (2025), 5660–5669
